作为北航传统艺能,进行了一手仙人掌的学。
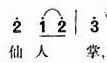
什么是仙人掌?
一个仙人掌要满足:图连通;每一条边最多位于一个简单环。注意,这种定义下的仙人掌允许重边(长度为 $2$ 的环)的存在。
当然,有的仙人掌还满足无重边,这样的仙人掌不存在长度为 $2$ 的环。
仙人掌有关问题通常有两类解决思路:DFS 树;圆方树。DFS 树的解决思路是根据仙人掌仅是在 DFS 树上加了几条链覆盖的性质,本文不讨论;本文重点讨论圆方树。
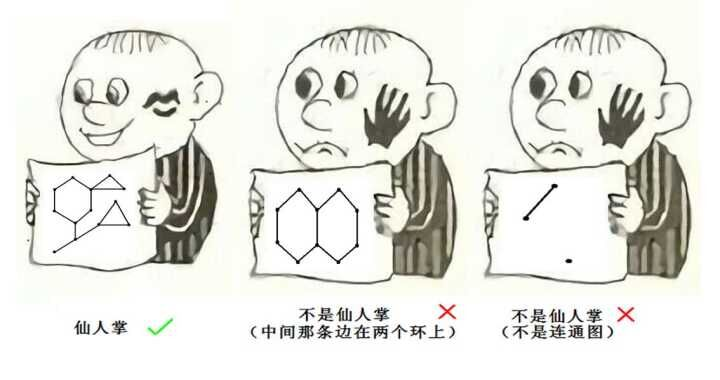
圆方树?
把仙人掌的每一个环变成一个方点,环中所有边删掉,对应顶点与方点连边;圆圆边不变,就获得了一棵圆方树。
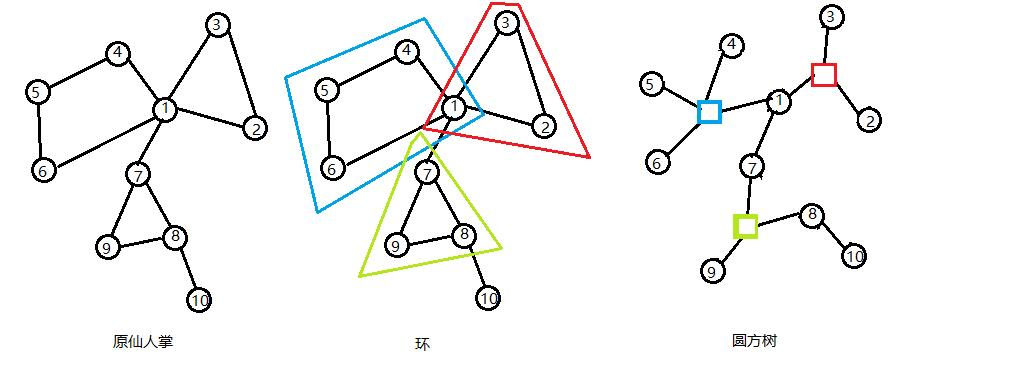
每个点存一下父亲信息,在 tarjan 的时候,对于一个点 $p$ ,如果其连接的子树 $q$ 在一个环内,则对整个环进行处理。光说太抽象,放代码:
1 | using T=modint; |
其中,G 是原图,adj 是圆方图。T 是边权的类型,可以根据具体情况设置。fa 是对每个点存储的,连向父亲的边(注意,不是父亲点,而是父亲边),此举的目的是处理带有重边(长度为 $2$ 的环)的仙人掌。
tarjan 有返回值,返回值表示原图是否为仙人掌。如果某个点的孩子里有两个或以上连向父亲的点(low[q]<dfn[p]),那么图不是仙人掌,代码中使用 ring 记录这样的点数。在这样记录的情况下,一个要重点注意的点是,tarjan 时,low[p]=min(low[p],dfn[q]) 不可写成 low[p]=min(low[p],low[q]),否则会影响到仙人掌的判定。
square_points 存储一些二元组 $(rt,q)$,一个二元组代表一个根为 rt,终点为 q 的环。当一个 $p$ 的孩子节点 $q$ 没有存父亲节点信息的时候,这个点是一个以 $p$ 为根的环的终点。如果题目没保证图是仙人掌,需要在判断了整张图是一个仙人掌后,对这些环进行处理,才能保证复杂度。
对于一个环,可以通过沿 $fa$ 一直跳获得上面的所有节点;后缀和存储在每个点或者边上,环的整体信息存在新的方点上,根上不存储信息。下面是一个后缀和记录距离的实现示例,至于到底记录什么,还需要具体题目具体分析:
1 | void add_square_point(int rt,int q,T w){ |
例题
对于仙人掌类型题目,先考虑在树上的情况,再进行环的处理。
求任意两点 $(u,v)$ 距离(洛谷 P5236 【模板】静态仙人掌)
考虑树的情况,每个节点 $p$ 只要记录一个从根到 $p$ 的距离,询问时查询 LCA 即可。
对于 LCA 是个圆点的情况,与树情况相同,仅需要考虑 LCA 是方点的情况,此时设两个环上对应点分别为 $A,B$,则答案即为 $dis(A,u)+dis(B,v)+dis(A,B)$,其中 $dis(A,B)$ 通过处理环的时候进行后缀和可以快速求得(是前缀和、后缀和的较小值)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int mod=998244353;
namespace cactus{
using T=int;
vector<pair<int,T>>G[N],adj[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
int vis[N];
pair<int,T> fa[N];
void add_cactus(int u,int v,T w){
adj[u].pb(mp(v,w));
adj[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
void add_edge(int u,int v,T w){
G[u].pb(mp(v,w));
G[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
int square_cnt=0,n=0;
// dis from rt to every q, only calculate points in the same ring
T dis[N];
T d[N]; // dis from 1 to i
void init(int _n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<=n+square_cnt;i++){
dfn[i]=low[i]=vis[i]=0;
G[i].clear();adj[i].clear();
fa[i]=mp(0,0);
}
tot=square_cnt=0;
n=_n;
}
// point square tree
vector<pair<pii,T>>square_points;
void add_square_point(int rt,int q,T w){
int cur=q;
T suf_sw=w;
int new_point=n+ ++square_cnt;
int cnt=1;
do{
dis[cur]=suf_sw;
auto pr=fa[cur];
suf_sw+=pr.se;
cur=pr.fi;
cnt++;
}while(cur!=rt);
dis[new_point]=suf_sw;dis[rt]=0;
cur=q;
do{
add_cactus(cur,new_point,min(suf_sw-dis[cur],dis[cur]));
cur=fa[cur].fi;
}while(cur!=fa[rt].fi);
}
int tarjan(int p,int f){ // return is cactus?
low[p]=dfn[p]=++tot;
vis[p]=1;
int rings=0;
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr.fi;
if(q==f)continue;
if(!dfn[q]){
fa[q]=mp(p,pr.se);
if(!tarjan(q,p))return 0;
low[p]=min(low[p],low[q]);
}
else if(vis[q])low[p]=min(dfn[q],low[p]);
if(low[q]>dfn[p])add_cactus(p,q,pr.se);
else if(low[q]<dfn[p]&&++rings>1)return 0;
}
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr.fi;
if(dfn[q]<=dfn[p]||fa[q].fi==p)continue;
square_points.pb(mp(mp(p,q),pr.se));
}
return 1;
}
// lca
int lg[N];
int dep[N];
int anc[22][N];
void dfs4lca(int p,int f){
dep[p]=dep[f]+1;
anc[0][p]=f;
int i;
for(i=1;(1<<i)<=dep[p];i++)anc[i][p]=anc[i-1][anc[i-1][p]];
for(auto pr:adj[p]){
int q=pr.fi;
if(q!=f)d[q]=d[p]+pr.se,dfs4lca(q,p);
}
}
void init_lca(int rt=1){
d[rt]=dep[rt]=0;
dfs4lca(rt,0);
int i;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)lg[i]=lg[i-1]+(1<<(lg[i-1]+1)==i);
}
pair<pii,int>lca(int x,int y){
int i;
assert(x<=n&&y<=n); // not square points
if(dep[x]<dep[y])swap(x,y);
while(dep[x]>dep[y])
x=anc[lg[dep[x]-dep[y]]][x];
if(x==y)return mp(mp(0,0),x); // not dealing this case!
for(i=lg[dep[x]];~i;i--)
if(anc[i][x]!=anc[i][y])
x=anc[i][x],y=anc[i][y];
return mp(mp(x,y),anc[0][x]);
}
void prepare_cactus(){
square_points.clear();
assert(tarjan(1,0));
for(auto pr:square_points)
add_square_point(pr.fi.fi,pr.fi.se,pr.se);
init_lca();
}
T query(int u,int v){
auto pr=lca(u,v);
int r=pr.se;
int a=pr.fi.fi,b=pr.fi.se;
if(r<=n)return d[u]+d[v]-2*d[r];
else{
if(dis[a]<dis[b])swap(a,b);
T ring_len=dis[r];
T len_ab=dis[a]-dis[b];
len_ab=min(len_ab,ring_len-len_ab);
return d[u]-d[a]+d[v]-d[b]+len_ab;
}
}
};
int main(){
int i,j,n,m,q;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
cactus::init(n);
for(i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u,v,w;
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
cactus::add_edge(u,v,w);
}
cactus::prepare_cactus();
while(q--){
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
printf("%d\n",cactus::query(u,v));
}
return 0;
}
求每个环的大小(洛谷 P4129 [SHOI2006]仙人掌)
双倍经验,需要写个高精。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int mod=998244353;
namespace high{
struct num{
int a[N];
int deg;
num(int x){
assert(x>=0&&x<=9);
a[deg=1]=x;
}
void recalc(){
while(deg&&a[deg]==0)deg--;
}
void print(){
recalc();
if(!deg)printf("0");
else for(int i=deg;i>=1;i--)printf("%c",a[i]+'0');
}
num& operator*=(const int x){
int i;
recalc();
for(i=1;i<=deg;i++)a[i]*=x;
for(i=1;i<=deg;i++){
if(a[i]>=10){
if(i==deg)a[++deg]=0;
a[i+1]+=a[i]/10;
a[i]%=10;
}
}
return *this;
}
};
}
namespace cactus{
high::num res(1);
using T=int;
vector<pair<int,T>>G[N],adj[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
int vis[N];
pair<int,T> fa[N];
void add_cactus(int u,int v,T w){
adj[u].pb(mp(v,w));
adj[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
void add_edge(int u,int v,T w){
G[u].pb(mp(v,w));
G[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
int square_cnt=0,n=0;
// dis from rt to every q, only calculate points in the same ring
T dis[N];
T d[N]; // dis from 1 to i
void init(int _n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<=n+square_cnt;i++){
dfn[i]=low[i]=vis[i]=0;
G[i].clear();adj[i].clear();
fa[i]=mp(0,0);
}
tot=square_cnt=0;
n=_n;
}
// point square tree
vector<pair<pii,T>>square_points;
void add_square_point(int rt,int q,T w){
int cur=q;
T suf_sw=w;
int new_point=n+ ++square_cnt;
int cnt=1;
do{
dis[cur]=suf_sw;
auto pr=fa[cur];
suf_sw+=pr.se;
cur=pr.fi;
cnt++;
}while(cur!=rt);
dis[new_point]=suf_sw;dis[rt]=0;
res*=(cnt+1);
cur=q;
do{
add_cactus(cur,new_point,min(suf_sw-dis[cur],dis[cur]));
cur=fa[cur].fi;
}while(cur!=fa[rt].fi);
}
int tarjan(int p,int f){ // return is cactus?
low[p]=dfn[p]=++tot;
vis[p]=1;
int rings=0;
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr.fi;
if(q==f)continue;
if(!dfn[q]){
fa[q]=mp(p,pr.se);
if(!tarjan(q,p))return 0;
low[p]=min(low[p],low[q]);
}
else if(vis[q])low[p]=min(dfn[q],low[p]);
if(low[q]>dfn[p])add_cactus(p,q,pr.se);
else if(low[q]<dfn[p]&&++rings>1)return 0;
}
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr.fi;
if(dfn[q]<=dfn[p]||fa[q].fi==p)continue;
square_points.pb(mp(mp(p,q),pr.se));
}
return 1;
}
void calc(){
int i;
res=high::num(1);
square_points.clear();
if(!tarjan(1,0)){
printf("0\n");
return;
}
for(auto pr:square_points)
add_square_point(pr.fi.fi,pr.fi.se,pr.se);
res.print();
}
};
int main(){
int T,n,m,i;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
cactus::init(n);
for(i=1;i<=m;i++){
int k;
scanf("%d",&k);
int u,v=-1;
while(k--){
scanf("%d",&u);
if(v!=-1)cactus::add_edge(u,v,0);
v=u;
}
}
cactus::calc();
return 0;
}
求直径(最远距离两点间的距离,不是最长路!)(洛谷 P4244 [SHOI2008]仙人掌图 II)
这一类树形 DP 问题,在
tarjan的时候就可以顺便全计算出来。考虑树上的情况。设 $f_i$ 表示以 $i$ 为根的子仙人掌最深有多深,对于普通点处理是容易的,$f_i=\max_{j\in son_i} f_j+1$,同时在计算过程中可以更新答案。对于一个环,需要将环上任意两点的贡献对答案进行更新,同时将最深的深度更新到这个环的根上。
考虑环两点 $i,j$,对答案的贡献为 $f_i+f_j+(dep_j-dep_i)=(f_i-dep_i)+f_j+dep_j$,于是将环摊开成两倍,枚举右端点,左端点单调队列维护一下即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int mod=998244353;
namespace cactus{
using T=int;
vector<int>G[N],adj[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
int vis[N];
int fa[N];
void add_cactus(int u,int v){
adj[u].pb(v);
adj[v].pb(u);
}
void add_edge(int u,int v){
G[u].pb(v);
G[v].pb(u);
}
int n=0,square_cnt=0;
int f[N];
int diam;
void add_square_point(int rt,int q){
int cur=q;
int new_point=n+ ++square_cnt;
do{
add_cactus(cur,new_point);
cur=fa[cur];
}while(cur!=fa[rt]);
}
void calc_dp(int rt,int p){
int i,hd=0,tl=0,t=p;
static int a[N];
while(t!=rt)a[++tl]=t,t=fa[t];
a[++tl]=rt;t=p;
int len=tl;
while(t!=rt)a[++tl]=t,t=fa[t];
static int q[N]; // decreasing queue
int qh=1,qt=0;
for(i=1;i<=tl;i++){
while(qh<=qt&&i-q[qh]>len/2)++qh;
if(qh<=qt)diam=max(diam,i+f[a[i]]+f[a[q[qh]]]-q[qh]);
while(qh<=qt&&f[a[q[qt]]]-q[qt]<f[a[i]]-i)qt--;
q[++qt]=i;
}
for(i=1;i<len;i++)
f[rt]=max(f[rt],f[a[i]]+min(i,len-i));
}
int tarjan(int p,int F){ // return is cactus?
low[p]=dfn[p]=++tot;
vis[p]=1;
int rings=0;
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr;
if(q==F)continue;
if(!dfn[q]){
fa[q]=p;
if(!tarjan(q,p))return 0;
low[p]=min(low[p],low[q]);
}
else if(vis[q])low[p]=min(dfn[q],low[p]);
if(low[q]>dfn[p]){
add_cactus(p,q);
diam=max(diam,f[p]+f[q]+1);
f[p]=max(f[p],f[q]+1);
}else if(low[q]<dfn[p]&&++rings>1)return 0;
}
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr;
if(dfn[q]<=dfn[p]||fa[q]==p)continue;
calc_dp(p,q);
}
return 1;
}
void init(int _n){
int i;
diam=0;
for(i=0;i<=n+square_cnt;i++){
dfn[i]=low[i]=vis[i]=0;
G[i].clear();adj[i].clear();
fa[i]=0;
}
tot=square_cnt=0;
n=_n;
}
void prepare_cactus(){
assert(tarjan(1,0));
}
};
int main(){
int i,j,n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
cactus::init(n);
for(i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u,v=0,k;
scanf("%d",&k);
while(k--){
scanf("%d",&u);
if(v)cactus::add_edge(u,v);
v=u;
}
}
cactus::prepare_cactus();
printf("%d\n",cactus::diam);
return 0;
}
一个正常一些的
DP(P3687 [ZJOI2017]仙人掌)给一个图,问有多少种加边方法,使得最终形成一个无自环无重边的仙人掌。
假做法:需要保证无重边,于是最开始想了个神秘树形 $DP$:设 $f_{0,p}$ 表示子树都没有边连上来,$f_{1,p}$ 表示子树有一个连到 $p$,$f_{2,p}$ 表示有两个连到 $p$。但是用点表示边很难表示全,有很多边界情况,于是做法假了。
正解:仙人掌本质还是把一个树用一些互不相交的链覆盖。于是先考虑树的情况,每个点连出 $deg_i$ 条边,其中需要两两配对或者有一些孤立点,对于一个固定度数可以求出方案数 $g_d$,其中 $g$ 是一个显然 $DP$: $g_n=g_{n-1}+g_{n-2}(n-1)$,注意到每一种配对形式都使得环的大小大于三,所以是对的。对于每个点的任意一种配对组合,都是一个合法的仙人掌,于是直接把每个点 $i$ 的 $g_{deg_i}$ 乘起来即为答案。仙人掌上,方点隔离开的各个树组成森林,森林每个树互不影响,乘积即为答案。(所以这个题甚至不需要用圆方树做)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int mod=998244353;
namespace cactus{
using T=int;
vector<int>G[N],adj[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
int vis[N];
int fa[N];
void add_cactus(int u,int v){
adj[u].pb(v);
adj[v].pb(u);
}
void add_edge(int u,int v){
G[u].pb(v);
G[v].pb(u);
}
int square_cnt=0,n=0;
void init(int _n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<=n+square_cnt;i++){
dfn[i]=low[i]=vis[i]=0;
G[i].clear();adj[i].clear();
fa[i]=0;
}
tot=square_cnt=0;
n=_n;
}
// point square tree
vector<pii>square_points;
void add_square_point(int rt,int q){
int cur=q;
int new_point=n+ ++square_cnt;
assert(new_point<N);
do{
add_cactus(cur,new_point);
cur=fa[cur];
}while(cur!=fa[rt]);
}
int tarjan(int p,int f){ // return is cactus?
low[p]=dfn[p]=++tot;
vis[p]=1;
int rings=0;
for(auto q:G[p]){
if(q==f)continue;
if(!dfn[q]){
fa[q]=p;
if(!tarjan(q,p))return 0;
low[p]=min(low[p],low[q]);
}
else if(vis[q])low[p]=min(dfn[q],low[p]);
if(low[q]>dfn[p])add_cactus(p,q);
else if(low[q]<dfn[p]&&++rings>1)return 0;
}
for(auto q:G[p]){
if(dfn[q]<=dfn[p]||fa[q]==p)continue;
square_points.pb(mp(p,q));
}
return 1;
}
ll h[N],g[N];
void dfs4dp(int p,int f){
ll prod=1;
int cnt=0;
vis[p]=1;
for(auto q:adj[p]){
if(q==f||q>n)continue; // square point
dfs4dp(q,p);
prod=prod*h[q]%mod;
cnt++;
}
if(!f)h[p]=prod*g[cnt]%mod;
else h[p]=prod*g[(cnt+1)]%mod;
}
ll calc(){
int i;
ll res=1;
square_points.clear();
if(!tarjan(1,0))return 0;
for(auto pr:square_points)add_square_point(pr.fi,pr.se);
for(i=0;i<=n+square_cnt;i++)vis[i]=h[i]=0;
g[0]=g[1]=1;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)g[i]=(g[i-1]+g[i-2]*(i-1)%mod)%mod;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)if(!vis[i]){
dfs4dp(i,0);
res=res*h[i]%mod;
}
return res;
}
};
int main(){
int T,n,m,i;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
cactus::init(n);
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
cactus::add_edge(u,v);
}
printf("%lld\n",cactus::calc());
}
return 0;
}
2019 牛客多校 6I Can They Go to Galar?
对仙人掌进行染色。点 $1$ 染色,之后进行扩散,边权表示扩散的概率。问期望有多少个点被染色。
根据期望可加性,求出每个点被染的概率再求和即可。设 $p_i$ 表示 $i$ 被染概率,在树上有 $p_i=p_{f_i}\cdot p_{e(f_i,i)}$,在以 $r$ 为根的边权为 $(e_1,e_2,\dots e_i,e_{i+1},\cdots e_k)$ 的环上有 $p_i=p_r(1-\prod_{j<i}e_j)(1-\prod_{j>i}e_j)$。
这是比较基础的 $dp$,求出圆方树后 $BFS$ 即可。环上处理的是后缀积,如果不处理前缀积,就要用到除法,为了避免除零,需要对加边进行筛选。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int mod=998244353;
ll qp(ll a,int p){
ll ans=1;
for(;p;p>>=1,a=a*a%mod)if(p&1)ans=ans*a%mod;
return ans;
}
struct modint{
ll a;
modint(){a=0;}
modint(ll x):a(x%mod){}
ll inv()const{assert(a);return qp(a,mod-2);}
modint operator*(const modint&x){return modint(a*x.a%mod);}
modint operator/(const modint&x){return modint(x.inv()*a%mod);}
modint operator+(const modint&x){return modint((a+x.a)%mod);}
modint operator-(const modint&x){return modint((a+mod-x.a)%mod);}
};
namespace cactus{
using T=modint;
vector<pair<int,T>>G[N],adj[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
int vis[N];
pair<pii,T> fa[N];
void add_cactus(int u,int v,T w){
adj[u].pb(mp(v,w));
adj[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
void add_edge(int u,int v,T w){
G[u].pb(mp(v,w));
G[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
int square_cnt=0,n=0;
T dis[N]; // dis from rt to every q, only calculate points in the same ring
T d[N]; // dis from 1 to i
int start[N]; // start of square points
vector<pair<pii,T>>square_points;
T prob[N];
void add_square_point(int rt,int q,T w){
int cur=q;
T suf_sw=w;
int new_point=n+ ++square_cnt;
start[new_point]=q;
do{
dis[cur]=suf_sw;
auto pr=fa[cur];
suf_sw=suf_sw*pr.se;
cur=pr.fi.fi;
}while(cur!=rt);
dis[new_point]=suf_sw;dis[rt]=0;
cur=q;
do{
add_cactus(cur,new_point,modint(0));
cur=fa[cur].fi.fi;
}while(cur!=fa[rt].fi.fi);
}
int tarjan(int p,int f){ // return is cactus?
low[p]=dfn[p]=++tot;
vis[p]=1;
int rings=0,i;
for(i=0;i<G[p].size();i++){
auto pr=G[p][i];
auto q=pr.fi;
if(q==f)continue;
if(!dfn[q]){
fa[q]=mp(mp(p,i),pr.se);
if(!tarjan(q,p))return 0;
low[p]=min(low[p],low[q]);
}
else if(vis[q])low[p]=min(dfn[q],low[p]);
if(low[q]>dfn[p])add_cactus(p,q,pr.se);
else if(low[q]<dfn[p]&&++rings>1)return 0;
}
for(i=0;i<G[p].size();i++){
auto pr=G[p][i];
auto q=pr.fi;
if(dfn[q]<=dfn[p]||(fa[q].fi.fi==p&&fa[q].fi.se==i))continue;
square_points.pb(mp(mp(p,q),pr.se));
}
return 1;
}
void init(int _n){
int i;
square_points.clear();
for(i=0;i<=n+square_cnt;i++){
dfn[i]=low[i]=vis[i]=0;
G[i].clear();adj[i].clear();
fa[i]=mp(mp(0,0),0);
}
tot=square_cnt=0;
n=_n;
}
ll calc(){
int i;
assert(tarjan(1,0));
for(auto pr:square_points)
add_square_point(pr.fi.fi,pr.fi.se,pr.se);
queue<int>Q({1});
for(i=1;i<=n+square_cnt;i++)vis[i]=0,prob[i]=0;
vis[1]=1;
prob[1]=1;
while(!Q.empty()){
int p=Q.front();Q.pop();
for(auto pr:adj[p]){
int q=pr.fi;
if(vis[q])continue;
if(q<=n)prob[q]=prob[p]*pr.se,vis[q]=1,Q.push(q);
else{
vis[q]=1; // ring
int t=start[q];
while(t!=p){
T one=modint(1);
prob[t]=prob[p]*(one-(one-dis[t])*(one-dis[q]/dis[t]));
vis[t]=1;Q.push(t);
t=fa[t].fi.fi;
}
}
}
}
T res=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)res=res+prob[i];
return res.a;
}
};
int main(){
int T,i,n,m,nCas=0;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
cactus::init(n);
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v,a,b;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&u,&v,&a,&b);
if(a)cactus::add_edge(u,v,modint(a*qp(b,mod-2)%mod));
}
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",++nCas,cactus::calc());
}
return 0;
}
2021 牛客多校 5A Away from College
给一个仙人掌,每次询问三个点 $c,d,l$,问在 $c-d,c-l$ 最短路上,且离 $c$ 最远的点。
三对点的 $lca$ 必定有两个相同,或三个都相同,于是可以转化成一个环上三个点的问题。每个点存的是距离后缀和,再简单讨论一下就可。此时 LCA 如果是方点,还要记录离两个点最近的圆点,而倍增求 $LCA$ 时会交换 $x,y$ ,需要注意!要记录是否被交换。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int mod=998244353;
namespace cactus{
using T=int;
vector<pair<int,T>>G[N],adj[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
int vis[N];
pair<int,T> fa[N];
void add_cactus(int u,int v,T w){
adj[u].pb(mp(v,w));
adj[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
void add_edge(int u,int v,T w){
G[u].pb(mp(v,w));
G[v].pb(mp(u,w));
}
int square_cnt=0,n=0;
int ring_root[N];
T dis[N]; // dis from rt to every q, only calculate points in the same ring
T d[N]; // dis from 1 to i
vector<pair<pii,T>>square_points;
void add_square_point(int rt,int q,T w){
int cur=q;
T suf_sw=w;
int new_point=n+ ++square_cnt;
int cnt=1;
do{
dis[cur]=suf_sw;
auto pr=fa[cur];
suf_sw+=pr.se;
cur=pr.fi;
cnt++;
}while(cur!=rt);
dis[new_point]=suf_sw;dis[rt]=0;
ring_root[new_point]=rt;
cur=q;
do{
add_cactus(cur,new_point,min(suf_sw-dis[cur],dis[cur]));
cur=fa[cur].fi;
}while(cur!=fa[rt].fi);
}
int tarjan(int p,int f){ // return is cactus?
low[p]=dfn[p]=++tot;
vis[p]=1;
int rings=0;
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr.fi;
if(q==f)continue;
if(!dfn[q]){
fa[q]=mp(p,pr.se);
if(!tarjan(q,p))return 0;
low[p]=min(low[p],low[q]);
}
else if(vis[q])low[p]=min(dfn[q],low[p]);
if(low[q]>dfn[p])add_cactus(p,q,pr.se);
else if(low[q]<dfn[p]&&++rings>1)return 0;
}
for(auto pr:G[p]){
auto q=pr.fi;
if(dfn[q]<=dfn[p]||fa[q].fi==p)continue;
square_points.pb(mp(mp(p,q),pr.se));
}
return 1;
}
// lca
int lg[N];
int dep[N];
int anc[22][N];
void dfs4lca(int p,int f){
dep[p]=dep[f]+1;
anc[0][p]=f;
int i;
for(i=1;(1<<i)<=dep[p];i++)anc[i][p]=anc[i-1][anc[i-1][p]];
for(auto pr:adj[p]){
int q=pr.fi;
if(q!=f)d[q]=d[p]+pr.se,dfs4lca(q,p);
}
}
void init_lca(int rt=1){
d[rt]=dep[rt]=0;
dfs4lca(rt,0);
int i;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)lg[i]=lg[i-1]+(1<<(lg[i-1]+1)==i);
}
pair<pii,int>lca(int x,int y){
int i,flag=0;
assert(x<=n&&y<=n); // not square points
if(dep[x]<dep[y])swap(x,y),flag=1;
while(dep[x]>dep[y])
x=anc[lg[dep[x]-dep[y]]][x];
if(x==y)return mp(mp(0,0),x); // not dealing this case!
for(i=lg[dep[x]];~i;i--)
if(anc[i][x]!=anc[i][y])
x=anc[i][x],y=anc[i][y];
if(flag)swap(x,y);
return mp(mp(x,y),anc[0][x]);
}
void init(int _n){
int i;
square_points.clear();
for(i=0;i<=n+square_cnt;i++){
dfn[i]=low[i]=vis[i]=0;
G[i].clear();adj[i].clear();
fa[i]=mp(0,0);
}
tot=square_cnt=0;
n=_n;
}
void prepare_cactus(){
assert(tarjan(1,0));
for(auto pr:square_points)
add_square_point(pr.fi.fi,pr.fi.se,pr.se);
init_lca();
}
T query_dis(int u,int v){
auto pr=lca(u,v);
int r=pr.se;
int a=pr.fi.fi,b=pr.fi.se;
if(r<=n)return d[u]+d[v]-2*d[r];
else{
if(dis[a]<dis[b])swap(a,b);
T ring_len=dis[r];
T len_ab=dis[a]-dis[b];
len_ab=min(len_ab,ring_len-len_ab);
return d[u]-d[a]+d[v]-d[b]+len_ab;
}
}
void query(int c,int d,int l){
auto cd=lca(c,d),cl=lca(c,l),dl=lca(d,l);
int cc,dd,ll,ring,x=0;
int disc,disd,disl;
if(cd.se==cl.se&&cl.se==dl.se){
ring=dl.se;
if(dl.se<=n)x=dl.se;
else{
cc=cd.fi.fi;disc=dis[cc];
dd=dl.fi.fi;disd=dis[dd];
ll=cl.fi.se;disl=dis[ll];
}
}else if(cd.se==cl.se){
ring=dl.se;
if(dl.se<=n)x=dl.se;
else{
cc=ring_root[dl.se];disc=0;
dd=dl.fi.fi;disd=dis[dd];
ll=dl.fi.se;disl=dis[ll];
}
}else if(cd.se==dl.se){
ring=cl.se;
if(cl.se<=n)x=cl.se;
else{
dd=ring_root[cl.se];disd=0;
cc=cl.fi.fi;disc=dis[cc];
ll=cl.fi.se;disl=dis[ll];
}
}else if(cl.se==dl.se){
ring=cd.se;
if(cd.se<=n)x=cd.se;
else{
ll=ring_root[cd.se];disl=0;
cc=cd.fi.fi;disc=dis[cc];
dd=cd.fi.se;disd=dis[dd];
}
}
if(!x){
int d1=disd-disc,d2=dis[ring]-d1;
int d3=disl-disc,d4=dis[ring]-d3;
if(d1<0)d1+=dis[ring],d2-=dis[ring];
if(d3<0)d3+=dis[ring],d4-=dis[ring];
int minlen=min(d1,d2)+min(d3,d4);
if(minlen==d1+d3)x=(d1<d3)?dd:ll;
else if(minlen==d2+d4)x=(d2<d4)?dd:ll;
else x=cc;
}
printf("%d %d\n",x,query_dis(x,c));
}
};
int main(){
int i,j,n,m,q;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
cactus::init(n);
for(i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
cactus::add_edge(u,v,1);
}
cactus::prepare_cactus();
while(q--){
int c,d,l;
scanf("%d%d%d",&c,&d,&l);
cactus::query(c,d,l);
}
return 0;
}